Introduction
Physiotherapy in West Vancouver for Foot
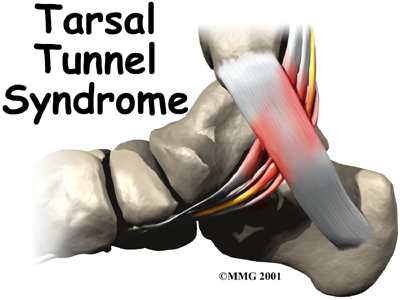
Welcome to West Vancouver Sports and Orthopedic Physiotherapy's patient resource about Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome.
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs from abnormal pressure on a nerve in the foot. The condition is similar to carpal tunnel syndrome in the wrist. The condition is somewhat uncommon and can be difficult to diagnose.
This guide will help you understand:
- where the tarsal tunnel is located
- how tarsal tunnel syndrome develops
- what can be done to treat the condition
#testimonialslist|kind:all|display:slider|orderby:type|filter_utags_names:Foot therapy|limit:15|heading:Hear from some of our *Foot Therapy* patients#
Anatomy
Where is the tarsal tunnel, and what does it do?
The runs into the foot behind the medial malleolus, the bump on the inside of the ankle. As it enters the foot, the nerve runs under a band of fibrous tissue called the flexor retinaculum. The flexor retinaculum is a dense band of fibrous tissue that forms a sort of tunnel, or tube. Several tendons, as well as the nerve, artery, and veins that travel to the bottom of the foot pass through this tunnel. This tunnel is called the tarsal tunnel. The tarsal tunnel is made up of the bone of the ankle on one side and the thick band of the flexor retinaculum on the other side.
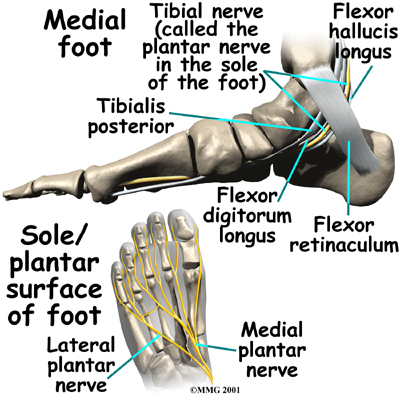
Related Document: West Vancouver Sports and Orthopedic Physiotherapy's Patient's Guide to Foot Anatomy
Causes
What causes tarsal tunnel syndrome?
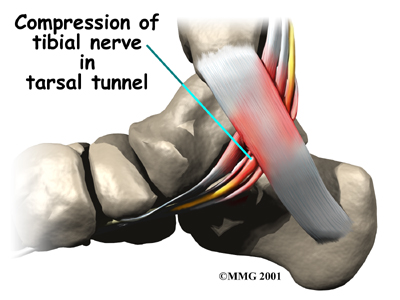 In many cases, doctors aren't sure what causes tarsal tunnel syndrome. Inflammation in the tissues around the tibial nerve may contribute to the problem by causing swelling in the tissues and on the nerve.
In many cases, doctors aren't sure what causes tarsal tunnel syndrome. Inflammation in the tissues around the tibial nerve may contribute to the problem by causing swelling in the tissues and on the nerve.
Anything that takes up space in the tarsal tunnel can increase pressure in the area because the flexor retinaculum cannot stretch very much. This can occur from swollen varicose veins, a tumor (noncancerous) on the tibial nerve, and swelling caused by other conditions, such as diabetes.
As pressure increases in the tarsal tunnel, the nerve is the most sensitive to the pressure and is squeezed against the flexor retinaculum.
This causes problems in the nerve that may lead to of tarsal tunnel syndrome.
In the case of a nerve, the area of skin supplied by the nerve usually feels numb, and the muscles controlled by the nerve may become weak. Pain is sometimes felt near the area where the nerve is squeezed or pinched.
Symptoms
What does tarsal tunnel syndrome feel like?
Tarsal tunnel syndrome usually causes a vague pain in the sole of the foot. Most patients describe this pain as a burning or tingling sensation. The symptoms are typically made worse by activity, especially standing and walking for long periods. Symptoms are generally reduced by rest. You may feel pain if you touch your foot along the course of the nerve. If the condition becomes worse, your foot may feel numb and weak.
Diagnosis
How do health care providers identify tarsal tunnel syndrome?
When you first visit West Vancouver Sports and Orthopedic Physiotherapy in West Vancouver our physiotherapist will begin by taking a complete history, and will perform a physical examination. We will also check to see if there are any signs that suggest nerve involvement.
Some patients may be referred to a doctor for further diagnosis. Once your diagnostic examination is complete, the physiotherapists at West Vancouver Sports and Orthopedic Physiotherapy have treatment options that will help speed your recovery, so that you can more quickly return to your active lifestyle.
Our Treatment
Non-surgical Rehabilitation
Treatment for this condition depends on what is contributing to the pressure on the nerve. Our physiotherapist can direct treatments to the painful area that help to control pain and swelling, such as ultrasound, moist heat, and soft-tissue massage. Physiotherapy sessions sometimes include iontophoresis, which uses a mild electrical current to push anti-inflammatory medicine, prescribed by your doctor, into the sore area.
 Once the swelling and inflammation have improved, our physiotherapist can design a program of stretching exercises to improve flexibility in the calf muscles and to encourage the tibial nerve to glide within the tarsal tunnel.
Once the swelling and inflammation have improved, our physiotherapist can design a program of stretching exercises to improve flexibility in the calf muscles and to encourage the tibial nerve to glide within the tarsal tunnel.
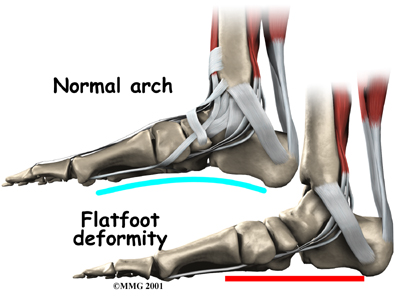
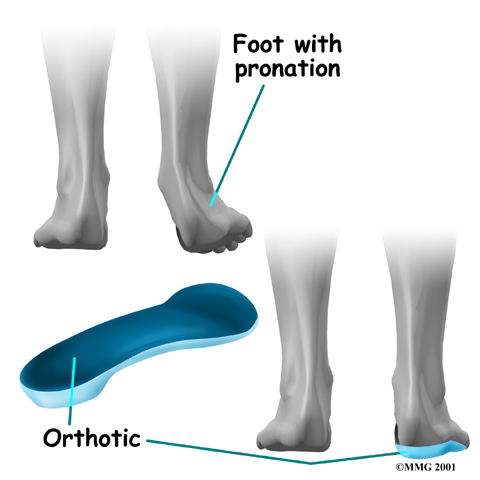
People who have problems of (flattened arches) may need specialized inserts, called orthotics, for their shoes.
Pronation is a common condition in which the inside edge of the foot rolls in, causing the arch to flatten. When this happens, the tibial nerve within the tarsal tunnel can become stretched.
If your tarsal tunnel syndrome is being aggravated by an abnormal position of the foot such as pronation, our physiotherapist may recommend to relieve the problem. Orthotics worn inside your shoe can help support the arch and take tension off the tibial nerve.
If your symptoms fail to respond to nonsurgical treatments, surgery to relieve the pressure on the tibial nerve may be suggested.
Post-surgical Rehabilitation
Pain and symptoms generally begin to improve with surgery, but you may have tenderness in the area of the incision for several months after the procedure.
Your ankle will be supported in a plaster splint for about 10 days after surgery. To help you begin your recovery, the physiotherapists at West Vancouver Sports and Orthopedic Physiotherapy in can teach you how to properly use crutches to keep from placing weight on your foot while you stand or walk.
You will be advised to keep the dressing on your foot until you return to your doctor for follow up, and to avoid getting the stitches wet. Your stitches will usually be removed 10 days after surgery, at which time you will switch to a supportive walking boot.
Your physiotherapist in West Vancouver will advise you to take time during the day to support your leg with the ankle and foot elevated above the level of your heart to promote the decrease of swelling. You will also be encouraged you to move your ankle and toes occasionally during the day.
Our physiotherapist may use ice packs, soft-tissue massage, and hands-on stretching to help with the range of motion in your ankle. When your stitches are removed, you'll begin doing exercises to help strengthen the muscles that support the ankle and arch. We may also use special stretches to encourage the tibial nerve to slide inside the tarsal tunnel.
When you are ready, our physiotherapist will provide you with new exercises designed to get your leg and ankle working in ways that are similar to the activities you do every day, such as rising on your toes, walking, and going up and down stairs.
Although the time required for recovery is different for each person, as a guideline you may expect to attend physiotherapy sessions for up to eight weeks after surgery, with full recovery taking several months.
When your recovery is well under way, your regular visits to West Vancouver Sports and Orthopedic Physiotherapy will end. Although we will continue to be a resource, you’ll eventually be in charge of doing your exercises as part of an ongoing home program.
West Vancouver Sports and Orthopedic Physiotherapy provides services for physiotherapy in West Vancouver.
Physician Review
Your doctor may advise doing a nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test to help diagnose your condition. This test measures how fast nerve impulses travel along a nerve. If the test shows that the impulses are traveling slowly across the ankle, this may confirm a diagnosis of tarsal tunnel syndrome.
If your doctor recommends nonsurgical treatment, you should begin to see some improvement in your symptoms within a few days. Anti-inflammatory medications may take up to seven to 10 days to become effective.
A cortisone shot usually works within 24 hours. A cortisone injection may give temporary relief of symptoms. The cortisone is injected into the tarsal tunnel so that it bathes the nerve and other tissues. This may decrease the inflammation and swelling of the tissues in the tarsal tunnel and reduce the irritation on the nerve.
Alterations to your shoe wear, such as using orthotics, may take several weeks to have an effect.
Surgery
The procedure to release the flexor retinaculum can usually be done using either a spinal type anesthetic or a general anesthetic. Once you have anesthesia, your surgeon will make sure the skin of your leg and ankle are free of infection by cleaning the skin with a germ-killing solution.
The surgeon then makes a small incision in the skin behind the inside ankle bone (medial malleolus). The incision is made along the course of the tibial nerve where it curves behind the malleolus. The nerve is located and released by cutting the flexor retinaculum. The surgeon will then surgically follow the nerve into the foot, making sure the nerve is free of pressure throughout its course.
The flexor retinaculum is left open to give the nerves more space. Eventually, the gap between the two ends of the flexor retinaculum fills in with scar tissue. Following surgery, the skin is repaired with stitches.
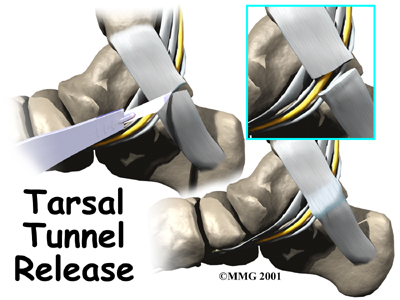
This surgery can usually be done on an outpatient basis, meaning you can leave the hospital the same day.
Portions of this document copyright MMG, LLC.







 In many cases, doctors aren't sure what causes tarsal tunnel syndrome. Inflammation in the tissues around the tibial nerve may contribute to the problem by causing swelling in the tissues and
In many cases, doctors aren't sure what causes tarsal tunnel syndrome. Inflammation in the tissues around the tibial nerve may contribute to the problem by causing swelling in the tissues and  Once the swelling and inflammation have improved, our physiotherapist can design a program of stretching exercises to improve flexibility in the calf muscles and to encourage the tibial nerve to glide within the tarsal tunnel.
Once the swelling and inflammation have improved, our physiotherapist can design a program of stretching exercises to improve flexibility in the calf muscles and to encourage the tibial nerve to glide within the tarsal tunnel.
